Photoelectric Effect
Photoelectric Effect: Overview
This topic covers concepts, such as, Photoelectric Effect, Stopping Potential for Photoelectrons, Photoelectric Effect and Wave Theory of Light & Secondary Electron Emission etc.
Important Questions on Photoelectric Effect
The stopping potential in an experiment on photoelectric effect is 1.5 V. The maximum kinetic energy of the photoelectron emitted would be:
The stopping potential in an experiment on the photoelectric effect is . The maximum kinetic energy of the photoelectron emitted would be
The stopping potential in an experiment on the photoelectric effect is . The maximum kinetic energy of the photoelectrons emitted would be
The maximum kinetic energy of a photoelectron is 3 eV. Its stopping potential is:
The Einstein’s photoelectric equation in terms of the stopping potential and the threshold frequency for a given photosensitive material is
The Einstein’s photoelectric equation is:
The Einstein’s photoelectric equation is:
The following graph shows the variation of stopping potential with frequency of the incident radiation for two photosensitive metals and .
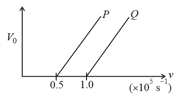
Which metal has
(i) a smaller threshold wavelength?
(ii) smaller kinetic energy?
The following graph shows the variation of stopping potential with the frequency of the incident radiation for two photosensitive metals and :
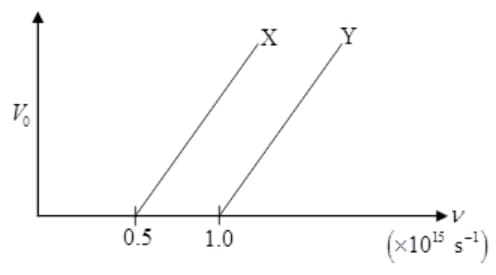
(i) Which of the metals has larger threshold wavelength? Give reason.
(ii) Explain, giving reason, which metal gives out electrons, having larger kinetic energy, for the same wavelength of the incident radiation.
The graph between frequency of incident radiations and stopping potential for a given photosensitive material is as follows.
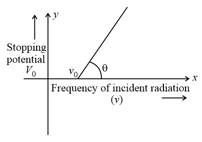
What information can be obtained from the value of the intercept on the potential axis?
The graph between frequency of incident radiations and stopping potential for a given photosensitive material is as follows.
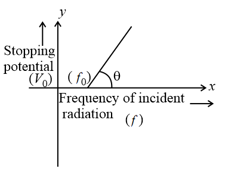
What information can be obtained from the value of the intercept on the potential axis?
Show graphically how the stopping potential for a given photosensitive surface varies with the frequency of the incident radiation.
In the photo-electron emission, the energy of the emitted electron is
The maximum kinetic energy of electrons emitted in the photoelectric effect is linearly dependent on the________________ of the incident radiation.
A Hydrogen-like atom has atomic number . Photons emitted in the electronic transitions from level to level in these atoms are used to perform photoelectric effect experiment on a target metal. The maximum kinetic energy of the photoelectrons generated is . If the photoelectric threshold wavelength for the target metal is , the value of is _____.
[Given and , where is the Rydberg constant, is the Planck’s constant and is the speed of light in vacuum]
When light of a given wavelength is incident on a metallic surface, the minimum potential needed to stop the emitted photoelectrons is . This potential drops to if another source with wavelength four times that of the first one and intensity half of the first one is used. What are the wavelength of the first source and the work function of the metal, respectively? [Take .]
Photons of wavelength fall on a metal surface whose work function is . Assume that each photoelectron inside the metal lattice may come out of the surface orcollide with the lattice before coming out. In each collision with the lattice, it loses of its existing energy. Which of the following can be a kinetic energy of an ejected photoelectron?
An -ray beam of monochromatic photon are incident on a metallic surface having a negligible work function (take). It is seen that the wavelength of most energetic photoelectrons is equal to the wavelength of -ray photons. Find the wavelength (in pm). Round off to nearest integer.
A light source emitting three wave lengths and has a total power of and a beam diameter . The power density is distributed equally among the three wavelengths. The beam shines normally on a metallic surface of area and having a work function of . Assume that each photon liberates an electron.
Figure shows a point light source placed in front of a conducting wall. All the ejected photoelectrons are immediately removed. Mark the correct statement.